Master international marketing opens the door to an expansive world where businesses can thrive beyond borders. In an era where globalization defines competitive advantage, understanding the nuances of international marketing is essential for any company looking to make a mark on the global stage. From recognizing the unique challenges of foreign markets to leveraging cultural insights, this journey delves into the myriad strategies that can enhance a brand’s international presence and appeal.
The significance of mastering international marketing lies not just in expanding reach, but in navigating the complex environment of diverse cultures, regulations, and consumer behaviors. Companies must differentiate their approaches to successfully engage with international audiences while overcoming potential obstacles that arise when entering new markets.
Importance of International Marketing
Mastering international marketing is crucial for businesses aiming to expand their reach and capitalize on global opportunities. As companies venture beyond domestic borders, they encounter diverse markets that require tailored strategies to address varying consumer behaviors, cultural nuances, and competitive landscapes. Understanding international marketing facilitates not only growth but also sustainable success in an interconnected global economy.The significance of international marketing lies in its ability to enhance brand visibility and create a competitive advantage in new markets.
Businesses that excel in this field can leverage unique selling propositions to attract and retain customers from different cultural backgrounds. International marketing differs fundamentally from domestic marketing in several key aspects, including market research, communication strategies, and distribution channels. Adapting to these elements is essential for effective engagement with international consumers.
As the world shifts towards sustainability, integrating solar panels into rooftop designs for a greener future is a crucial step. This approach not only harnesses renewable energy but also maximizes space efficiency on rooftops. By combining aesthetic appeal with environmental responsibility, modern architecture can play a vital role in promoting a sustainable lifestyle.
Key Differentiators of International Marketing
Several factors set international marketing apart from its domestic counterpart. Recognizing these distinctions is vital for businesses looking to thrive in global markets:
- Market Research Complexity: International markets often exhibit varied consumer preferences, requiring comprehensive research to understand local demands and trends. For instance, McDonald’s adapts its menu offerings to reflect local tastes, such as serving McAloo Tikki in India.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Understanding cultural nuances is paramount in international marketing. Brand messaging must resonate with local values and customs. For example, advertisements that are successful in one country may be considered offensive in another.
- Legal and Regulatory Challenges: Each country has its own legal framework, including advertising regulations, import/export restrictions, and labor laws. Companies must navigate these complexities to ensure compliance and foster good relationships with local governments.
- Currency and Pricing Strategies: Fluctuating exchange rates can impact pricing strategies significantly. Companies must develop flexible pricing models that account for currency risks, such as Coca-Cola’s pricing adjustments based on local economic conditions.
- Distribution and Logistics: Establishing efficient distribution channels is more challenging on an international scale. Businesses need to consider local infrastructure, transportation costs, and partnerships with local distributors to ensure product availability.
Challenges of Entering Foreign Markets
Entering foreign markets presents numerous challenges that require strategic planning and adaptation. Companies must be prepared to face various obstacles that can hinder their success.One significant challenge is understanding and adapting to local customer preferences, which may differ greatly from those in domestic markets. For example, brands may need to alter their product formulations or marketing approaches to align with local tastes.
Additionally, logistical hurdles such as customs regulations and supply chain complexities can impede the timely delivery of goods.
“Failing to understand the cultural and operational intricacies of a new market can result in costly missteps for businesses.”
Furthermore, competition in international markets can be intense, with local players often having an established presence and understanding of consumer behavior. Companies must invest in creating a unique value proposition to differentiate themselves effectively.In summary, mastering international marketing is essential for companies aiming to succeed in the global arena. By recognizing the key differentiators and potential challenges, businesses can develop robust strategies that foster growth and sustainability in diverse markets.
Strategies for Effective International Marketing
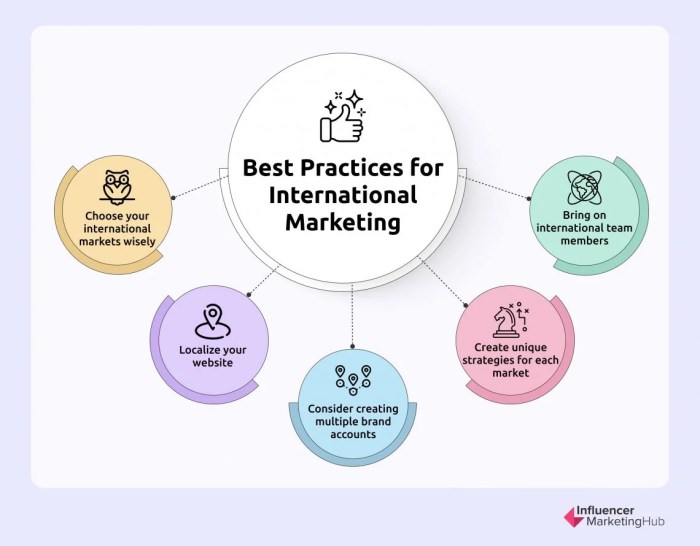
International marketing requires a strategic approach that considers cultural differences, market dynamics, and consumer behavior across various regions. To achieve success in global markets, businesses must employ diverse strategies that are tailored to the unique characteristics of each target audience. This section Artikels effective strategies for international marketing, delving into both traditional and digital methodologies, while also showcasing companies that have successfully navigated cultural adaptations in their marketing efforts.
Traditional Marketing Strategies Versus Digital Marketing Strategies
When businesses expand internationally, they often face the dilemma of choosing between traditional and digital marketing strategies. Both approaches have their own merits and applications in different markets. Traditional marketing techniques, such as print advertising, television commercials, and radio spots, often rely on broader outreach methods and are sometimes perceived as more credible by certain demographics.Conversely, digital marketing strategies, which include social media, email campaigns, and search engine optimization, offer precise targeting and measurable results.
The shift towards digital has been accelerated by the global connectivity provided by the internet, allowing companies to reach diverse audiences efficiently.
- Traditional Marketing Strategies:
- Print Advertising: Utilizing newspapers and magazines to reach older demographics or regions with limited internet access.
- Television Commercials: Engaging storytelling that resonates with local cultures, enhancing brand recognition.
- Outdoor Advertising: Billboards and transit ads in high traffic areas that capture attention in physical spaces.
- Digital Marketing Strategies:
- Social Media Marketing: Leveraging platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and TikTok to create engaging content suitable for local audiences.
- Email Marketing: Personalized communication that respects cultural nuances and preferences.
- Search Engine Optimization (): Tailoring website content to meet the search behavior of different regions, ensuring visibility on local search engines.
Examples of Companies Adapting Marketing Strategies for Different Cultures
Successful international marketing often hinges on a company’s ability to adapt its strategies to align with local cultures and consumer preferences. Numerous global companies have demonstrated this prowess through innovative marketing campaigns that respect and celebrate cultural diversity.
“Cultural adaptability in marketing is not just about translation; it’s about transcreation.”
One notable example is McDonald’s, which tailors its menu items to cater to local tastes. In India, McDonald’s offers a vegetarian menu featuring items like the McAloo Tikki burger, reflecting the dietary preferences of a large portion of the population. Similarly, in Japan, McDonald’s has introduced unique offerings such as the Teriyaki Burger, which resonates with local flavors.Coca-Cola also exemplifies effective cultural adaptation.
The company has crafted localized advertising campaigns that resonate with consumers in different markets. For instance, Coca-Cola’s “Share a Coke” campaign personalized bottles with names, fostering a sense of connection and community among consumers across various cultures.These examples underscore the importance of understanding and integrating cultural nuances in international marketing strategies to achieve success in diverse markets.
When considering the harsh realities of winter, exploring rooftop heating solutions for colder climates becomes essential. These innovative systems not only enhance comfort but also contribute to energy efficiency, ensuring that homes remain warm during the coldest months. By investing in such technologies, homeowners can significantly reduce heating costs while improving overall living conditions.
Cultural Considerations in International Marketing

Understanding cultural differences is crucial for any brand aiming to expand its reach beyond domestic borders. Cultural nuances can significantly influence consumer behavior, preferences, and perceptions of a brand. As businesses craft their international marketing strategies, recognizing and respecting these differences can lead to successful engagements and sustainable relationships with diverse markets.Cultural differences manifest in various ways, including language, customs, values, and social norms.
These elements shape how marketing messages are interpreted and what resonates with consumers. For instance, a marketing campaign that works well in one country may flop in another if it fails to align with local cultural contexts. Brands must be adaptable and culturally aware to avoid miscommunication and to foster trust with their audience.
Impact of Cultural Differences on Marketing Strategies
Cultural differences can dictate various aspects of marketing strategies, from messaging to product design. When entering a new market, brands must consider the following factors that illustrate the depth of cultural influences:
- Language Variations: Language not only involves translation but also the connotation and emotional impact words carry. A phrase that is catchy in English might be offensive or meaningless in another language.
- Symbolism and Imagery: Colors and symbols can have different meanings across cultures. For example, while white symbolizes purity in many Western cultures, it is often associated with mourning in some Eastern cultures.
- Consumer Behavior: Cultural norms influence buying habits. In collectivist cultures, group opinions may weigh more heavily than individual preferences, affecting how marketing messages should be framed.
Designing Marketing Campaigns for Diverse Cultural Audiences
Creating effective marketing campaigns for varied cultural audiences requires extensive research and tailored approaches. Understanding the local culture, traditions, and consumer expectations leads to more relevant and effective messaging. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Market Research: Conduct thorough research to identify cultural trends and consumer preferences. Utilize local focus groups to gain insights into the cultural landscape.
- Localized Content: Adapt marketing materials to reflect local language and customs. This includes everything from advertisements to product packaging that resonates with local aesthetics.
- Collaborate with Local Influencers: Partnering with local influencers can enhance brand credibility. Influencers understand their audience and can effectively communicate brand messages in a culturally relevant manner.
Dos and Don’ts in Different Cultural Environments
Navigating diverse cultural environments requires a careful approach to avoid pitfalls that could harm a brand’s reputation. Understanding the appropriate actions to take can significantly enhance a brand’s success in international markets. Here are essential dos and don’ts:
- Dos:
- Do engage in active listening to understand local consumer needs and sentiments.
- Do respect local customs and traditions in both marketing messages and interactions.
- Do invest in language training for your team to facilitate better communication.
- Don’ts:
- Don’t assume that a winning strategy in one country will work in another without modification.
- Don’t use humor that could be misinterpreted across cultural lines.
- Don’t overlook local regulations regarding advertising and promotions.
Successful international marketing hinges on the brand’s ability to connect with consumers on a cultural level, making cultural competence a non-negotiable aspect of marketing strategies.
Legal and Ethical Aspects of International Marketing
International marketing is a complex field that intertwines with various legal and ethical considerations. As companies expand their operations beyond domestic borders, they encounter a myriad of regulations that can impact their marketing strategies. Understanding these legal frameworks and ethical standards is crucial for ensuring compliance and maintaining a positive brand reputation in diverse markets.Legal regulations play a pivotal role in shaping international marketing practices.
Each country has its own set of laws governing advertising, consumer protection, competition, and intellectual property rights. These regulations can vary significantly from one jurisdiction to another, necessitating thorough research and adaptation by companies seeking to market their products internationally.
Legal Regulations Affecting International Marketing
The legal landscape for international marketing encompasses several key regulations that businesses must adhere to in order to operate successfully in foreign markets. These regulations often include:
- Advertising Standards: Different countries have specific laws regarding what constitutes truthful advertising, including restrictions on misleading claims and the use of certain imagery. For example, in the European Union, advertising must comply with the Unfair Commercial Practices Directive, which prohibits deceptive advertising.
- Consumer Protection Laws: Many nations have strong consumer protection laws that require businesses to provide clear information about products and services, safeguarding consumer rights. In the United States, the Federal Trade Commission enforces regulations to protect consumers against unfair practices.
- Data Protection Regulations: With the rise of digital marketing, data privacy laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU dictate how companies can collect, store, and use consumer data. Non-compliance can result in heavy fines and legal repercussions.
- Intellectual Property Laws: Protecting intellectual property (IP) is critical in international marketing. Businesses must understand the IP laws in each country to avoid infringement issues, as seen in cases involving trademark disputes across borders.
Ethical Considerations in International Marketing
Ethics in international marketing extend beyond legal compliance; they involve understanding and respecting cultural differences and consumer expectations. Companies must approach international marketing with a commitment to ethical standards, which can manifest in several ways:
- Cultural Sensitivity: Marketing messages should resonate with local cultures, avoiding stereotypes or offensive content. Brands like Dove have faced backlash for campaigns perceived as culturally insensitive, highlighting the importance of understanding local customs.
- Transparency: Ethical marketing practices demand honesty and transparency in communication with consumers. Companies like Johnson & Johnson have built trust through transparent product information, especially in times of crisis.
- Environmental Responsibility: Increasingly, consumers expect brands to demonstrate environmental stewardship in their marketing efforts. Sustainable practices, such as those adopted by Patagonia, influence consumer perceptions and brand loyalty.
- Fair Labor Practices: Brands must ensure that their marketing does not exploit labor in their supply chain. Companies like Nike have faced criticism and legal challenges for labor violations in overseas factories, prompting a reevaluation of their marketing messages and corporate responsibility.
Case Studies of Legal and Ethical Issues
Several high-profile case studies illustrate the consequences of neglecting legal and ethical considerations in international marketing. These examples provide critical insights into the potential pitfalls companies may face.
- Coca-Cola’s “Happiness Factory” Campaign: This campaign faced scrutiny for its portrayal of workers in international bottling plants. Critics argued that the portrayal was unrealistic and obscured labor issues, prompting Coca-Cola to revisit its messaging and emphasize transparency in its operations.
- Nestlé and the Baby Formula Controversy: Nestlé faced global backlash for its aggressive marketing of infant formula in developing countries, which many viewed as unethical. The company has since implemented stricter guidelines and promoted responsible marketing practices.
- Volkswagen Emissions Scandal: Volkswagen’s misleading marketing about the environmental performance of its vehicles led to significant legal penalties and reputational damage. This case underscores the importance of honesty in marketing communications.
Future Trends in International Marketing: Master International Marketing

As the global marketplace continues to evolve rapidly, businesses must adapt their marketing strategies to remain competitive. The future of international marketing is influenced by several key trends, including technological advancements, changing consumer behaviors, and the pressing need for sustainability. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for companies aiming to thrive in an increasingly interconnected world.The integration of technology and innovation will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of international marketing strategies.
Companies that leverage digital tools and platforms can enhance their reach and engagement across diverse markets. In this context, the following aspects will define the trajectory of international marketing:
Technological Integration in Marketing Strategies, Master international marketing
The rise of technology has transformed how companies interact with consumers and execute marketing campaigns. Businesses are turning to innovative solutions to leverage data and personalize their marketing efforts effectively. Key technological trends influencing international marketing include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being utilized to analyze consumer data, predict trends, and automate customer interactions, improving overall efficiency and customer satisfaction.
- Big Data Analytics: The ability to gather and analyze vast amounts of data allows companies to understand market dynamics and consumer preferences on a granular level, leading to more targeted marketing efforts.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): These technologies offer immersive experiences that can engage consumers in new ways, enhancing product visualization and driving purchasing decisions.
- Social Media Marketing: With platforms evolving continuously, businesses are required to innovate their social media strategies, focusing on authentic engagement and influencer partnerships to reach younger demographics.
The rapid advancement of these technologies presents opportunities for businesses to enhance their international marketing strategies and create deeper connections with global consumers.
Importance of Sustainability in International Marketing
As consumers become more environmentally conscious, sustainability is increasingly becoming a crucial aspect of international marketing. Companies must align their values and practices with the expectations of consumers who prioritize eco-friendly products. Integrating sustainability into marketing strategies can significantly affect brand perception and customer loyalty. Businesses should consider the following components to establish a sustainable approach:
- Eco-friendly Products: Developing products that minimize environmental impact can attract eco-conscious consumers and differentiate brands in competitive markets.
- Transparent Supply Chains: Communicating the ethical sourcing and production practices can enhance trust and credibility, especially among consumers prioritizing corporate responsibility.
- Community Engagement: Businesses that engage with local communities and contribute positively can foster goodwill and create a loyal customer base.
- Digital Sustainability: Embracing sustainable practices in digital marketing, such as optimizing website energy efficiency and using green hosting services, can support broader environmental goals.
By adopting sustainable marketing practices, companies can not only appeal to a growing segment of environmentally aware consumers but also contribute to global sustainability initiatives.
Framework for Adapting to Emerging Trends
To effectively navigate the changing landscape of international marketing, businesses need a structured approach that emphasizes agility and responsiveness. The following framework can help organizations adapt to emerging trends in the international marketplace:
- Market Research: Constantly analyze global market trends and consumer behaviors to identify opportunities and threats.
- Continuous Innovation: Foster a culture of innovation within the organization, enabling teams to develop and test new ideas quickly.
- Cross-Cultural Training: Equip marketing teams with cultural insights and awareness to effectively navigate diverse markets and tailor messaging accordingly.
- Collaborative Partnerships: Establish alliances with local businesses and influencers to enhance market entry strategies and increase brand visibility.
Implementing this framework will enable companies to remain resilient and relevant in the face of evolving international marketing trends, ensuring long-term success in a dynamic global marketplace.